IEEE Wireless Local Area Networks (RF-LANs) - ppt download
$ 11.99 · 4.9 (543) · In stock

Wireless Networks Wireless communication is one of the fastest-growing technologies. The demand for connecting devices without the use of cable is increasing everywhere. Wireless LANs can be found in on college campuses, Bus stations, Railway Stations, Airport, in office buildings, and in many public areas.
IEEE Wireless Local Area Networks (RF-LANs)
Architetcure: The standard defines two kind of services: BSS and ESS. Basic Service Set(BSS): IEEE defines a BSS as the building blocks of wireless LANs. A BSS is made of stationary or mobile wireless stations and an optional central base station called, Access Point.
In this architecture, stations can form a network without the need of an AP, they can locate one another and agree to be part of a BSS. A BSS with an AP is sometimes referred to as an infrastructure network.
In this case, the BSSs are connected through a distributed system, which is usually a wireless LAN. The distributed system connects the APs in the BSSs. The ESS uses two types of stations: mobile and stationary. The mobile stations are normal stations inside a BSS. The stationary stations are AP stations that are part of a wired LAN.
Types of Wireless LANs Infrastructure (BSS and ESS) Ad-hoc (BSS)
IEEE defines the physical (PHY), logical link (LLC) and media access control (MAC) layers for a wireless local area network networks can work as. basic service set (BSS) extended service set (ESS) BSS can also be used in ad-hoc networking. Network. LLC MAC. FHSS. PHY. DSSS. IR. DS, ESS. LLC: Logical Link Control Layer. MAC: Medium Access Control Layer. PHY: Physical Layer. FHSS: Frequency hopping SS. DSSS: Direct sequence SS. SS: Spread spectrum. IR: Infrared light. BSS: Basic Service Set. ESS: Extended Service Set. AP: Access Point. DS: Distribution System. ad-hoc network.
Hidden Terminal Problem. Station B has a transmission range shown by the left oval and every station in this range can hear any signal transmitted by station B. Station C has a transmission range shown by the right oval and every station in this range can hear any signal transmitted by station C. Station C is outside the transmission range of B; similarly, station B is outside the transmission range of C. Station A can hear both the transmission of B and C.
Before sending a frame, the source station senses the medium by checking the energy level at the carrier frequency. The channel uses a persistence strategy with back-off until the channel is idle. After the station is found to be idle, station waits for a period of time called the distributed inteeframe space (DCF), then station sends a control frame called the request to send (RTS).
extends the On-line period. Installation on difficult-to-wire areas. inside buildings. road crossings. Increased reliability. Note: Pay attention to security! Reduced installation time. cabling time and convenient to users and difficult-to-wire cases.
54 Mbps for a/g (GSM:9.6Kbps, HCSCD:~40Kbps, GPRS:~160Kbps, WCDMA:up to 2Mbps) Long-term cost savings. O & M cheaper that for wired nets. Comes from easy maintenance, cabling cost, working efficiency and accuracy. Network can be established in a new location just by moving the PCs!
Date Speed. IEEE b support up to 11 MBps, sometimes this is not enough - far lower than 100 Mbps fast Ethernet. Interference. Works in ISM band, share same frequency with microwave oven, Bluetooth, and others. Security. Current WEP algorithm is weak - usually not ON! Roaming. No industry standard is available and propriety solution are not interoperable - especially with GSM. Inter-operability. Only few basic functionality are interoperable, other vendor’s features can’t be used in a mixed network.
Lack of wireless networking experience for most IT engineer. No well-recognized operation process on network implementation. Selecting access points with ‘Best Guess’ method. Unaware of interference from/to other networks. Weak security policy. As a result, your WLAN may have. Poor performance (coverage, throughput, capacity, security) Unstable service. Customer dissatisfaction.
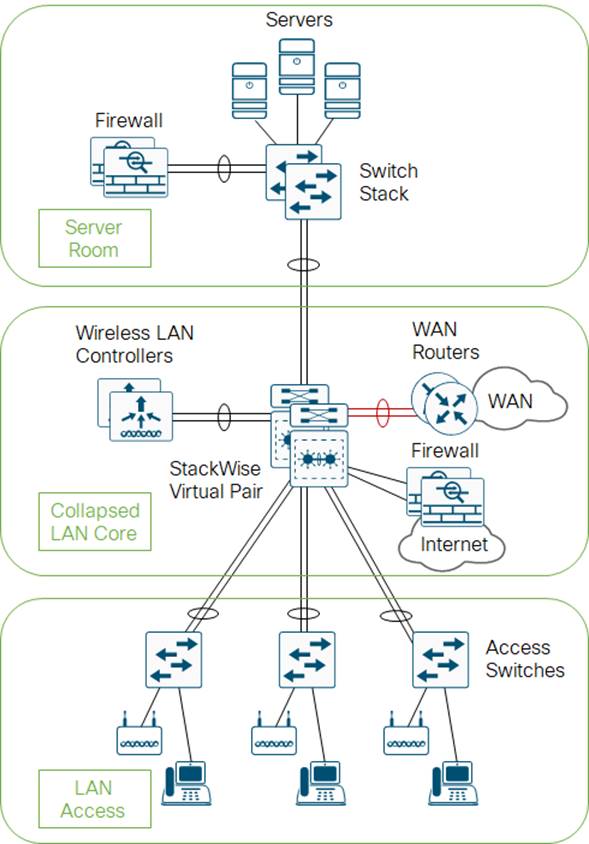
Campus LAN and Wireless LAN Solution Design Guide - Cisco

PPT - Wireless LAN & IEEE 802.11 PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:3703817
PPT – IEEE 802.11 Wireless Local Area Networks (RF-LANs) PowerPoint presentation

IEEE Wireless Local Area Networks (RF-LANs) - ppt download
Wireless Body Area Network PowerPoint Template - PPT Slides
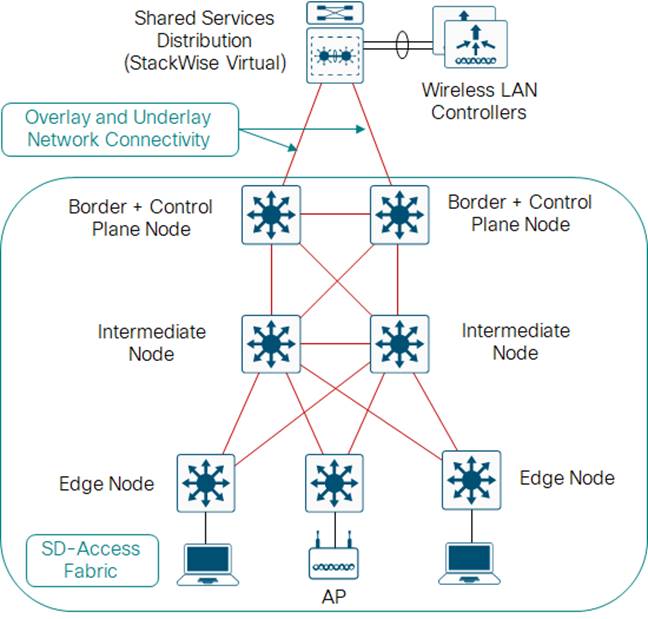
Campus LAN and Wireless LAN Solution Design Guide - Cisco

PPT - Wireless LANs and PANs PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:4251393
Wireless Protocol, PDF, Wireless Lan

Wireless network - Wikipedia

PPT - Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN) Part-1: IEEE802.11 PowerPoint Presentation - ID:5788290

